Projects
Fundamental insights into the kinetic behavior of supported metallocene catalysts
 Albaraa S. Falodah, a.s.m.falodah@uu.nl
Albaraa S. Falodah, a.s.m.falodah@uu.nl
Sponsor: SABIC, since July 2020
Supervisors: prof. dr. ir. Bert Weckhuysen, prof. dr. Eelco Vogt
Metallocene catalysts, Heterogeneous catalysis, In-situ spectroscopy
In our quest for polymers with superior and specialized properties, and better recyclability, better olefin polymerization catalysts are sought.
Metallocene catalysts hold great promises that are yet to be fulfilled. These zirconium (or hafnium) based catalysts are highly active, and are highly tunable through employing different ligands around the metal, and the use of co-catalysts (Fig. 1). The resulting activity in olefin polymerization can be orders of magnitude higher than catalysts of other types when used as homo-geneous catalysts.
A major challenge in utilizing these catalysts is the discrepancy (and/or deterioration) in their performance when they are transformed from homogeneous to heterogeneous catalysts. Heterogeneous catalysts are preferred by industry following decades of optimizing processes and plants around catalysts like Ziegler-Natta and Phillips catalysts to produce polyolefins. Additionally, the “single-site” character of these catalysts results in polymers that are more difficult to process into final products.
Advanced spectroscopic techniques are utilized in this project to examine the kinetic effects resulting from supporting candidate industrial metallocene catalysts. These insights are coupled with performance and activity studies in industrial settings. The aim is to explain the difference in behavior between supported (heterogeneous) and unsupported (homogeneous) metallocene catalysts.
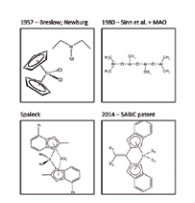
Figure 1: The evolution of metallocene catalysts for polyolefin polymerization, shown through examples.
[1] Breslow, D. S. et al., JACS 79 (18), 5072-5073 (1957)
[2] Sinn, H., et al., Angew. Chem. – Int. Ed. 19, 390-392 (1980)
[3] Severn, J. R. et al., Chem. Rev. 105, 4073−4147 (2005)
[4] Al-Shammari, H. et al., patent WO2014139949A1, (2014)

